eBook
Six Components of Successful Data Governance
Read this eBook to learn how most organizations understand that their business assets should include investments in technology, people, and infrastructure. Companies wisely develop and implement formal policies and processes to govern these assets and ensure a maximum return on investment.
However, when it comes to one of an enterprise’s greatest resources, organizations often fall short. We’re talking about data – or what Forbes describes as “your most valuable and ignored asset.” It is a proverbial gorilla in the room for many organizations.
Businesses frequently fail to properly invest in their data, and even fewer have implemented a formal Data Governance strategy. This is partly due to a lack of understanding of the nuances of data management, as well as the benefits derived from the combination of Data Governance, Data Quality, and Data Stewardship.
In this e-book, we’ll discuss the different sides of Data Governance, and describe the six critical components of a successful implementation.

Data Management vs. Data Governance
First, let’s distinguish between data management and Data Governance. Data management is often assumed to mean Data Governance, when in fact, the two are different.
The broader term of data management is best described as the logistics of managing your data. It is characterized by a set of standard tools for collecting, validating, storing, organizing, protecting, processing, and otherwise maintaining your data.
On the other hand, Data Governance encompasses a business-driven program and involves a cross-functional process for maximizing the value of data, while also minimizing the risk of poor data.
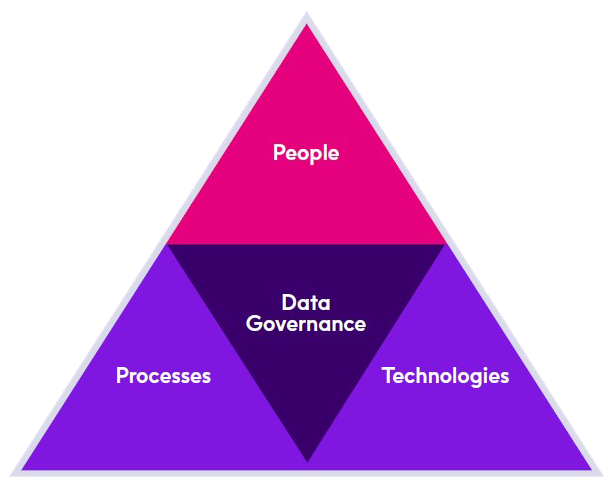
Imagine Data Governance as the convergence of People, Process, and Technology. It is about consensus building, ownership, and overcoming parochial barriers. It not only aligns IT and business functions to leverage the benefits of data, but also defines data ownership and policies, decision rights, and escalation procedures.
To sum things up, successful Data Governance determines who owns the data, how and by whom data is created and updated, and who arbitrates decisions when disagreements or needs arise.
Master Data Management
What is the role of Master Data Management (MDM)?
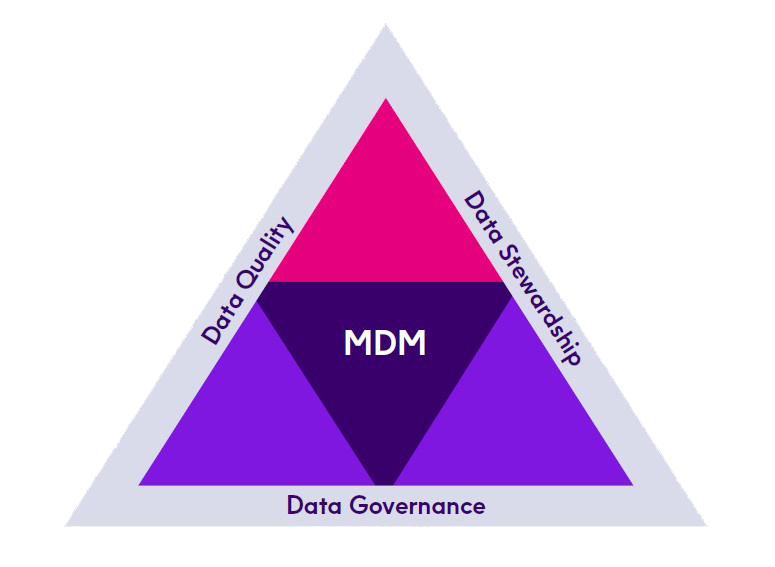
Many businesses are strategically turning to an end-to-end Master Data Management (MDM) solution to establish a single view of data. An MDM solution with integrated Data Governance functionality and data stewardship tools allows organizations to operate with seamless integration and synchronization.
With the appropriate MDM technology, businesses can:
- Create a “golden record” for data entities by integrating databases and systems such as ERP, CRM, WMS, and OMS, as well as hard-to-integrate legacy systems that are difficult to access and even more cumbersome to decommission.
- Dramatically enhance data quality with the ability to extract, load, publish, and syndicate accurate and consistent content to internal and external recipients.
- Create Data Governance policies and workflows.
- Help companies adapt and comply with expanded and evolving regulations.
- Improve the efficiencies and effectiveness of business intelligence and enterprise processes that rely on high-quality, accurate information.
In the following sections, we’ll discuss the six essential components for successful Data Governance; address the critical roles of data quality and data stewardship; and explain how MDM supports a thriving Data Governance program.
– Ted Friedman, Gartner
Six Steps to Data Governance
When developing a Data Governance program, there are six essential components to consider:
Your Data Governance processes should exhibit transparency. Participants should clearly see how and when datarelated decisions and controls are introduced into those processes. Of course, by transparency we are not suggesting an absence of security; instead, we are proposing that for any data-related activity, the appropriate people should be able to discover what activities are taking place.
If the focus of your program is something other than compliance, it is easy to forget that others may need to review your work and decisions. You must strike a balance here. Data-related decisions, processes, and controls subjected to your Data Governance program must be auditable and include the necessary documentation to support compliance based and operational auditing requirements.
Accountability is often lacking or confusing when you begin developing your documentation. However, your Data Governance program must define responsibilities for cross-functional data-related decisions, processes, and controls. Use this opportunity to look for situations where nobody appears to be accountable, or many groups are listed as responsible for addressing gaps and overlaps in currently perceived accountabilities.
In defining accountabilities, you will need to introduce checks-and-balances between business and technology teams, as well as between those who create/collect data, those who manage it, those who use it, and those who introduce standards and compliance requirements. Establishing appropriate checks-and-balances can be invaluable in guiding active participation in your program.
Achieving data standardization is a prerequisite for many high-value business and IT projects. Therefore, your Data Governance program will need to address standardization, where appropriate, of enterprise data. You must closely evaluate the primary uses of your organization’s data and focus on data normalization in those specific scenarios.
A Data Governance program must support both proactive and reactive change management activities for reference data values and the structure/use of master data and metadata. For example, when a new regulation is introduced that requires compliance, or your company acquires a business with data that doesn’t yet match your existing model/structure. Simply put, if your desire is for sustainable success in projects that involve data, then you need to control how and when that data changes. Likewise, with a Data Governance program in support of an MDM project, you need to account for not only data changes but underlying changes to the data model, taxonomy, and beyond.
Competitive benefits of a successful data governance program:
- Increases the value of the data to the business.
- Reduces operational friction.
- Ensures regulatory compliance.
- Defines standard processes for addressing data issues.
- Provides transparency of data ownership and responsibilities.
MDM For Data Governance
One of the most significant benefits of MDM lies in the effectiveness of Data Governance. Moving data out of silos and into a central repository puts Data Governance in the spotlight for increased accuracy and transparency.
According to DATAVERSITY, “With Multi-domain MDM solutions, it is much easier to ensure that standards are being met since there is only
one repository for the master data. Users will have substantially less autonomy in creating definitions and rules for data, since the overall architecture will be simplified, resulting in greater transparency. As a result of better principles of governance, cross-functional collaborations between departments is more likely to occur, resulting in increased efficiency and better resource allocation.”
This level of governance puts companies in a position to transform data into insights to drive better decision-making and long-term transformation.
- Improve accuracy and accountability by providing clear ownership of data creation and publication process.
- Facilitate transparent monitoring of the content creation and business processes.
- Reduce regulatory compliance risk.
- Maintain brand continuity over multiple channels.
Establishing Data Quality Standards
An essential element in a Data Governance program is the accompanying processes and tools that ensure data quality. Data and digital content are in extremely high demand, yet it can be challenging to acquire and manage this content consistently. Businesses that rely on data and information must work to validate, learn, track, and strategize to ensure continuous data quality. Doing so requires the following crucial data quality components:
1) Data Accuracy
Data accuracy is critical in today’s omnichannel environment. For example, when considering a purchase, 71 percent of online buyers rely on product information and content,3 and over a third of consumers say they would not purchase a product if they did not trust the product information displayed. Establishing accurate data relies on golden record management and automated processes that reduce error-prone processes.
2) Data Usability
Even accurate data lacks impact if it’s not usable. Usability boils down to delivering the right data in the right way to extract the most value. Data usability is even more critical now that organizations rely on data pools such as GDSN, IDEA, ACES, PIES, and other several other industry-specific standards to drive omnichannel and digital strategies.
3) Data Consistency
Ensuring data consistency across an organization – and to all recipients of your data – greatly improves your bottom line and increases overall customer satisfaction. Data consistency processes also help eliminate manual tasks in getting data to different recipients.
4) Data Completeness
What benchmarks or attributes are mandatory for your organization? Data completeness helps organizations uncover data gaps, prioritize (or “weigh”) data/attributes, and create thresholds for deliverables (i.e. pushing new products to market faster). Data completeness reflects an organization’s overall Data Governance strategy and how the company eliminates the manual processes in sending data.
MDM For Data Quality
Successful data quality measures require more than just transforming and normalizing data when it is first introduced to an MDM platform. Enterprises need holistic tools that enable the business to improve the quality of content it manages about products, customers, locations and more throughout the content lifecycle.
- Proactively detect and capture bad data.
- Validate bad data automatically, in real time or batch, based on pre-built or customized business rules.
- Track data quality issues requiring manual corrections in real time – from the time they are discovered to when they are corrected.
- Quickly see where data discrepancies or problems exist within data values through the use of an intuitive colorcoded user interface.
- Golden Record Management
- Cleansing
- Data Analysis
- Match, Merge, Link
- Harmonization
- Survivorship
- Compliance
- Fuzzy Matching
- Validation
- Profiling
- Reporting/Monitoring/Alerts
MDM for Data Stewardship
Finally, even with all of the safeguards available to prevent data issues from being introduced, data stewardship is required to manually monitor and resolve any data inconsistencies that arise.
Data stewardship encompasses the accountability and responsibility for ensuring effective control and use of data assets – both as a function and through the role of “data stewards.”
An MDM solution can provide the necessary support for data stewardship by equipping information stewards with the tools to monitor, analyze, and improve master data.
- Support stewards with policy and procedure enablement with an easy-to-use, web-based, graphical UI.
- Equip data stewards with a configurable workspace that displays only tasks assigned to them.
- Take advantage of built-in algorithms for matching and linking, including survivorship rules.
- Monitor stewardship processes with advanced logging and audit trails.
- Documenting rules and standards.
- Managing metadata.
- Tackling data quality issues.
- Setting and managing guidelines around data.
- Tracking performance and regulatory compliance.
- Reducing risk regarding data security and privacy.
- Defining processes, policies, and roles.
Where to Begin
Developing a robust Data Governance program – supported by data quality tools and data stewardship support – helps organizations leverage trusted data as a strategic asset and competitive differentiator in our data-driven world.
Are you ready to implement an effective Data Governance program?
- With EnterWorks MDM, your organization can integrate databases and systems, cleanse and consolidate data, match and merge entries, standardize data, and ensure Data Governance and stewardship support.
- Amplifi provides best-in-class strategy, consultancy and implementation services to help companies build out the right processes for each and every unique organization to ensure a successful information management solution that addresses all business cases, including MDM, Change Management, Data Governance, and analytics.
- Revolutionary Agile Data Fabric™ technology weaves together data domains
- Business-friendly platform for high user adoption, no coding required
- Hosted private cloud SaaS, your private cloud, on-premise, or hybrid
- Perpetual, term, and SaaS licenses
- Lowest total cost of ownership
- Highest customer satisfaction scores (Gartner® and Forrester®)
- Fastest go-live times in the industry